It is possible for a person to lose their hearing in several ways. Some hearing loss can be age-related, genetic, or caused by environmental factors. Depending on which part of your hearing is damaged, there are also different types of hearing loss.
Further, hearing loss can have different levels of severity and some frequencies may be more affected by hearing loss than others. The hearing loss can appear on the audiogram in different ways depending on the frequency of the hearing loss. There are, for example, high-frequency hearing loss, low-frequency hearing loss and mid-frequency hearing loss, also known as cookie-cutter hearing loss.
3 Types of Hearing Loss
How are the different types of frequencies shown on an audiogram? An audiogram is a standardized chart used by hearing health professionals to enter hearing thresholds and other audiometric values. It is also the baseline for hearing aid fitting.
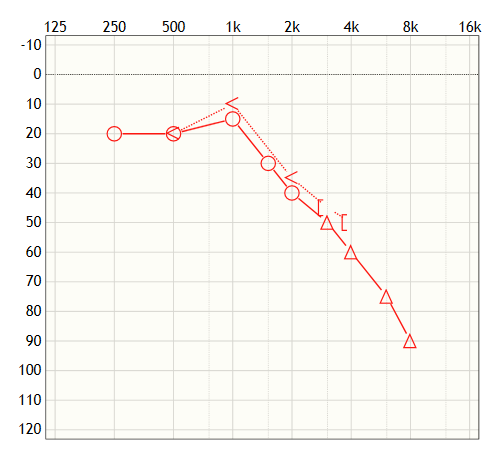
High frequency hearing loss
For high frequency hearing loss, people may notice more difficulty understanding female and child voices compared to male voices, as well as difficulty hearing birds singing. High frequency hearing loss can also be referred to as ski slope hearing loss because of the shape it takes when entered into the audiogram.
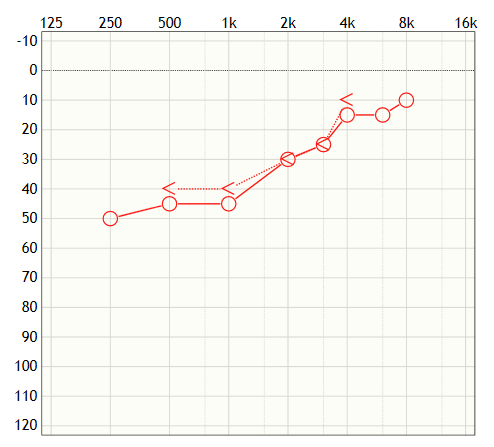
Low frequency hearing loss
In the case of low frequency hearing loss, people may find it challenging to understand male voices and may perceive music as being too small. This type of hearing loss can be described as reverse slope hearing loss.
Mid-frequency hearing loss
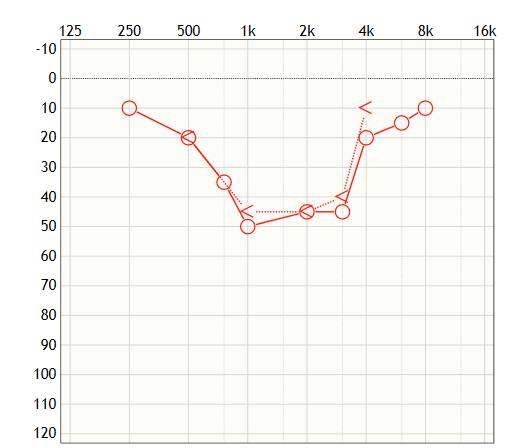
Mid-frequency hearing loss is often described as cookie bite hearing loss. When plotted on an audiogram, it looks like a cookie that has been bitten into. However, this name is misleading because there is nothing “sweet” about this type of hearing loss. Let’s discuss cookie bite hearing loss further and how it affects overall hearing.
What is cookie bite hearing loss?
According to research published in the Journal of Laryngology and Otology, cookie-cutter hearing loss is usually sensorineural and hereditary. Sensorineural hearing loss is permanent hearing loss, caused by damage to the inner ear or hearing nerve. However, the etiology may have other causes, such as a benign tumor called an auditory neuroma or vestibular nerve sheath tumor. This type of tumor occurs on the main nerve that runs from the inner ear to the brain.
How does cookie bite hearing loss sound like?
Cookie bite hearing loss can affect the mid-frequency range of hearing. Usually, this does not affect high-frequency hearing or low-frequency hearing. As a result, some sounds may seem louder while others may seem quiet or dull, resulting in an uneven and confusing interpretation of sounds in the surroundings.
Many human voices and music fall into this medium range, putting a strain on social interactions. Listening to TV or listening to music at standard volume after a conversation may be difficult. You may experience reduced intelligibility.
How is it diagnosed?
An audiological evaluation can help determine the diagnosis of a cookie bite hearing loss. If the loss is congenital, something you were born with, then this may first be noticed when your child has a hearing test. If the loss progresses over time, it may take longer for individuals to realize that their hearing has deteriorated. This may result in a delay in seeking treatment. In this case, those around you, the people you interact with the most, may suspect that you are having difficulty hearing before you realize it.
How can it be treated?
Unfortunately, there is no cure for sensorineural hearing loss. There are no medications or surgery that can restore hearing to normal. However, there are treatment options that can improve your hearing condition. For example, changing your communication habits and/or wearing hearing aids.
Changes in communication habits include using visual cues, adjusting where you sit at your desk or in the classroom, and reducing unwanted background noise. Hearing aids can be programmed and personalized to fit individual prescriptions and hearing needs. Combining these adaptations can improve quality of life, reconnect individuals to their hearing world, and reduce the potential negative effects of hearing loss.
In conclusion, not all hearing loss is the same. Treatment will depend on the type of hearing loss and your hearing needs. If you notice difficulty communicating or if you feel that your hearing has changed, have your hearing checked. Receiving routine hearing care and working with a hearing care professional will help determine the best solution for you.
Further Reading:
BEWARE OF SENSORINEURAL HEARING LOSS AND HOW TO SPOT THEM
SUMMARY OF COMMON AUDIOLOGY TERMS EXPLAINED
THE EXPERIENCE OF WEARING A HEARING AID FOR THE FIRST TIME
WHAT ARE THE FUNCTIONS OF HEARING AIDS?
Post time: Dec-17-2021